Past Retreats: 2013 Image Competition Entries
Click to view larger images.
Competition Winner:
Valerie Virta, PhD
Section on Vertebrate Development (Tom Sargent Lab)
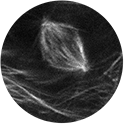
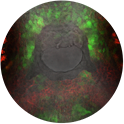
Dividing cell: The lines are microtubules, visualized in the living embryos via GFP fused to tubulin. These are epithelial cells located over the yolk ball. One cell is shown dividing as the microtubules have arranged into the mitotic spindle.
Monica Gupta, PhD
Section on Molecular Genetics of Immunity (Keiko Ozato Lab)
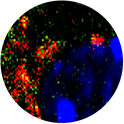
Below is the image of Bone marrow derived Macrophage infected with Gram positive bacteria Listeria monocytogenes (in Red). In Macrophages infection with Listeria induces the phenomenon of Autophagy, an intracellular event that act as an innate cellular defense mechanism to kill invading bacteria. In this image we can see that most of the Intracellular bacteria are trapped in Autophagosomes (in Green), which is a unique structure formed during Autophagy.
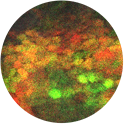
Suh Young Jeong, PhD
Section on Human Iron Metabolism (Tracey Rouault Lab)
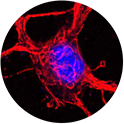
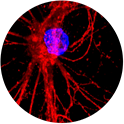
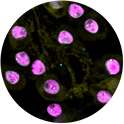
1) and 2) A mouse embryonic spinal cord neuron is visualized using two antibodies against neurofilaments (red). DAPI (blue) shows nucleus.
Annika Paukner, PhD
Laboratory of Comparative Ethology (Stephen Suomi Lab)
(Photo credit: Samantha Haynie) Juvenile male monkeys engage in rough-and-tumble play, a behavior of interest at the LCE Field Station in Poolesville, MD. Researchers here study complex social interaction in monkeys with respect to kinship, dominance hierarchy, and physiology.
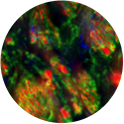
Mikolaj Sulkowski, PhD
Unit on Cellular Communication (Mihaela Serpe Lab)
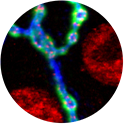
Larval insect central nervous system expressing Mad-GFP and stained against pMad and Elav.
Mikolaj Sulkowski, PhD
Unit on Cellular Communication (Mihaela Serpe Lab)
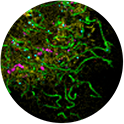
Insect neuromuscular junction.
Alex Valm, PhD, and Sarah Cohen, PhD
Section on Organelle Biology (Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz Lab)
A mouse embryonic fibroblast cell expressing fluorescent proteins that localize to peroxisomes (cyan), mitochondria (green), the endoplasmic reticulum (yellow), and lysosomes (red). The cell is also labeled with a dye that labels lipid droplets (magenta).
Alex and Sarah also submitted an accompanying movie (QuickTime format; to view, please download the QuickTime player or VLC Player).
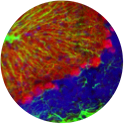
Valerie Virta, PhD
Section on Vertebrate Development (Tom Sargent Lab)
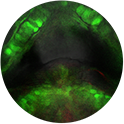
Arches with neuron: The green is GFP expressed under the Sox10 promoter, which highlights neural crest cells. In this view, neural crest cells have differentiated into 2 cell types in particular. There are columnar cartilage cells forming the larval jaw, and a neural cell is highlighted in the brain. The faint red is an indicator of Bmp signaling via Kusabira Orange expressed under Bmp Response Elements (BRE).
Valerie Virta, PhD
Section on Vertebrate Development (Tom Sargent Lab)
GreenBMP_RedCNCC: This image shows three types of fluorescence using 2 colors in a live zebrafish embryo. A ventral view of the face depicts the mouth opening, the stomodeum, using detection of regular light so that anatomical features can be located with respect to the fluorescent components of the image. The semicircles on either side of the stomodeum are the eyes, and differentiating pigment cells autofluoresce in the red channel as spidery shapes. The green cells express an indicator of Bmp signaling via GFP expressed under Bmp Response Elements. The red cells around the stomodeum are visualized via membrane-associated RFP expressed under the Sox10 promoter, which highlights neural crest cells. Depending on the strength of the signal, some cells show both a red outline and a green fill, indicating they are neural crest cells experiencing Bmp signaling. Using these living fish, Bmp signaling can be observed during morphogenesis of craniofacial neural crest cells forming the zebrafish jaw elements.
Valerie Virta, PhD
Section on Vertebrate Development (Tom Sargent Lab)
MonetFace: This image shows green fluorescence of neural crest cells via GFP expressed under the Sox10 promoter, and red fluorescence of cells experiencing Bmp signaling via Kusabira Orange expressed under Bmp Response Elements. Cells that look yellow or orange are neural crest cells actively engaged in Bmp signaling. Using these living fish, Bmp signaling can be observed during morphogenesis of craniofacial neural crest cells forming the zebrafish jaw elements.
Ian Williams, PhD
Section on Molecular Dysmorphology (Forbes Porter Lab)
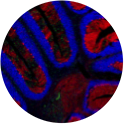
Astrogliosis in the cerebellum of mice with the lysosomal disease Niemann-Pick type C1 (GFAP astroglia in green, Purkinje neurons in red, dapi in blue).
Ian Williams, PhD
Section on Molecular Dysmorphology (Forbes Porter Lab)
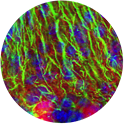
Myelination in the hindbrain of mice with the lysosomal disease Niemann-Pick type C1 (Myelin Basic Protein in green, Calbindin positive axons in red).
Ian Williams, PhD
Section on Molecular Dysmorphology (Forbes Porter Lab)
Anterior to posterior patterned Purkinje cell death and microgliosis in the cerebellum of mice with the lysosomal disease Niemann-Pick type C1 (microglia in green, Purkinje neurons in red, DAPI staining in blue).
Ian Williams, PhD
Section on Molecular Dysmorphology (Forbes Porter Lab)
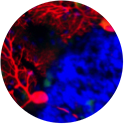
Example of Purkinje cell neurodegeneration in the lysosomal disease Niemann-Pick type C1 (Purkinje cells in red, microglia in green, DAPI staining in blue).
Ian Williams, PhD
Section on Molecular Dysmorphology (Forbes Porter Lab)
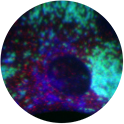
Cholesterol accumulation in the acidic compartment of lysosomal storage disease human fibroblasts (Unesterified Cholesterol in blue, lysosomes in green).
Ian Williams, PhD
Section on Molecular Dysmorphology (Forbes Porter Lab)
Astrogliosis in the cerebellum of mice with the lysosomal disease Niemann-Pick type C1 (GFAP astroglia in green, Purkinje neurons in red, dapi in blue).